
Net metering allows customers with a photovoltaic solar installation to send surplus unused energy back to the electrical grid in exchange for credits.
For example, with Hydro-Québec, when you produce more energy than you consume, the surplus is exported to the grid (your neighbors!) and credited to your account.
Most roofs can support the installation of solar panels, but factors such as orientation, tilt, shading, and roof structure can affect energy production.
An assessment by a professional is recommended to determine the suitability of your roof.
Solar systems generally require little maintenance. It is recommended to periodically check the panels to ensure they are clean and free of obstructions, and to have the electrical system checked annually to ensure it is functioning properly.
There are primarily two types of solar energy:
- thermal solar, which uses the heat from the sun to heat water or air for use in building heating or hot water,
- photovoltaic (PV) solar, which converts sunlight into electricity.
Each province has its own rules for net metering.
In Ontario, for example, the Net Metering Program allows consumers to credit their surplus solar energy against their consumption, thus reducing their electricity bill.
Solar shelters and gazebos offer a dual advantage: they create a shaded and comfortable outdoor space while also generating clean energy through the integration of solar panels, which enhances energy production productivity and efficiency. These structures are particularly advantageous for optimizing available space and reducing electricity bills by using bifacial solar panels that capture light from both sides, significantly increasing the amount of generated energy.
Solar panels can generate electricity on cloudy days, but their efficiency will be reduced. They do not produce electricity at night.
PV solar panels convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. When sunlight hits these cells, it generates an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect.
Monocrystalline panels are made from a single silicon crystal, allowing them to be more efficient but often at a higher cost. Polycrystalline panels are made from silicon fragments, making them less expensive but also slightly less efficient.
The incentives vary from province to province. They may include subsidies, rebates, and tax credits.
It is recommended to consult local or national resources for the most up-to-date information.
Most roofs can support the installation of solar panels, but factors such as orientation, tilt, shading, and roof structure can affect energy production.
An assessment by a professional is recommended to determine the suitability of your roof.
Solar shelters and gazebos offer a dual advantage: they create a shaded and comfortable outdoor space while also generating clean energy through the integration of solar panels, which enhances energy production productivity and efficiency. These structures are particularly advantageous for optimizing available space and reducing electricity bills by using bifacial solar panels that capture light from both sides, significantly increasing the amount of generated energy.
There are primarily two types of solar energy:
- thermal solar, which uses the heat from the sun to heat water or air for use in building heating or hot water,
- photovoltaic (PV) solar, which converts sunlight into electricity.
PV solar panels convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. When sunlight hits these cells, it generates an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect.

Monocrystalline panels are made from a single silicon crystal, allowing them to be more efficient but often at a higher cost. Polycrystalline panels are made from silicon fragments, making them less expensive but also slightly less efficient.
Yes, solar energy can be stored in batteries for use when the sun is not shining, thus allowing for continuous power supply, especially in off-grid systems or in on-grid systems equipped with energy storage solutions.
A solar system with batteries is environmentally friendly, requires minimal maintenance, and ensures a constant electricity supply (without interruptions). This makes it a perfect alternative to traditional generators, which are noisy, expensive, polluting, and often require maintenance, in addition to causing brief power outages when starting up.
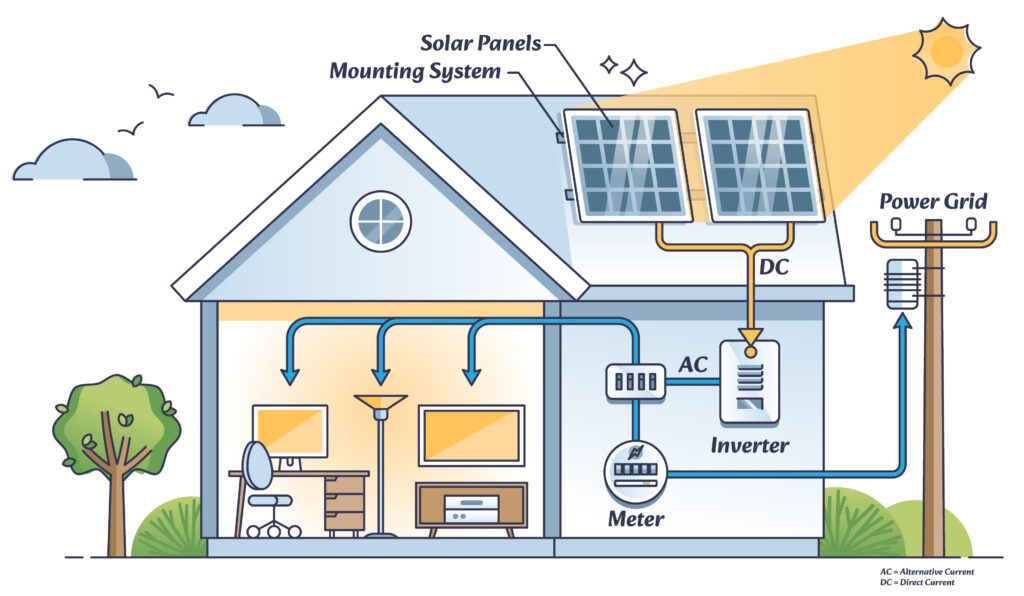
An on-grid solar system is connected to the public electrical grid. It provides electricity to a home or business and sends any surplus solar production back to the grid, often for credit or compensation. The mechanism for accounting for this energy is called "net metering."
By integrating batteries into a grid-connected solar system, one can not only practice "peak shaving" by using stored energy during peak consumption to reduce demand on the electrical grid, but also participate in consumption reduction challenges if the electricity provider allows it (for example, with Hydro-Québec's Hilo challenges).
An off-grid solar system operates independently and is not connected to the public electrical grid. It is typically used in remote areas and requires batteries to store solar energy for use outside of sunlight hours.
The energy from the batteries can be used at any time, depending on the programming of the inverter, especially if the power provided by the solar panels is insufficient during peak consumption even in sunlight hours.
This type of solar system is used in cottages, hunting camps, fishing camps, and other dwellings in remote or off-grid areas without electrical infrastructure.
Net metering allows customers with a photovoltaic solar installation to send surplus unused energy back to the electrical grid in exchange for credits.
For example, with Hydro-Québec, when you produce more energy than you consume, the surplus is exported to the grid (your neighbors!) and credited to your account.
Each province has its own rules for net metering.
In Ontario, for example, the Net Metering Program allows consumers to credit their surplus solar energy against their consumption, thus reducing their electricity bill.
The incentives vary from province to province. They may include subsidies, rebates, and tax credits.
It is recommended to consult local or national resources for the most up-to-date information.
Solar systems generally require little maintenance. It is recommended to periodically check the panels to ensure they are clean and free of obstructions, and to have the electrical system checked annually to ensure it is functioning properly.
Solar panels can generate electricity on cloudy days, but their efficiency will be reduced. They do not produce electricity at night.
Solar panels have a minimal environmental impact compared to other energy sources. They generate clean, renewable energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, the materials used in solar panel manufacturing are recyclable, which helps reduce waste and improves their overall ecological footprint.
Monofacial solar panels capture sunlight from one side and are the most common types used in residential and commercial installations. They are designed to directly absorb sunlight and convert this energy into electricity.
In contrast, bifacial solar panels can capture sunlight from both sides, both the top and the bottom. This allows them to produce 5% to 25% more electricity under the same sunlight conditions, as they can also absorb light reflected by the ground or other surfaces. They are particularly effective in areas with high reflection, such as on white or clear surfaces, or in installations where they are elevated to capture reflection.
The size of your solar system will depend on several factors including your energy needs, available space for panels, orientation and tilt of your roof, and your budget. It is generally recommended to consult with a professional for accurate assessment and design.
Solar systems are typically designed to last at least 25-30 years.
Performance may decrease slightly over time, but many remain productive well beyond this period.
Any more questions?
Feel free to fill out a quote request, that way we can provide you with advice.
Quote request